bpf_check
在bpf_check函数中,会按照顺序依次做如下check:

check_subprogs
先看check_subprogs:
static int check_subprogs(struct bpf_verifier_env *env) |
先是对整个程序进行逐条指令检查,遇到 jmp|call 之后就要add_subprog;(注意最开始把主程序入口0add进去了)具体来看,感觉就是根据jmp|call划分基本块;
然后针对每一个subprog(基本块)为一个基本单位,逐条指令进行分析,如果不是跳转类指令(jmp、call)就跳过,分析下一条指令;
如果是,则判断目标地址有没有超出当前基本块的范围;
最后在每个subprog的结尾处判断其结尾指令是否是exit或者跳转;
check_cfg
从头开始分析指令,维护一个insn_stack用于DFS搜索,维护一个insn_state用于表示每一条指令的状态;然后开始DFS搜索,每次取栈顶元素进行分析,每一类跳转指令都要考虑将后续的点进行push_insn,然后如果之前discover过,那么就要标记这个地方是可考虑prune的。
/* non-recursive depth-first-search to detect loops in BPF program |
调用push_insn如果返回0,表示遇到了一个DISCOVERED的地址,那么就要调用init_explored_state,标记为可考虑优化;
do_check_subprogs
static int do_check_subprogs(struct bpf_verifier_env *env) |
do_check_common
遍历所有的subprog,然后调用do_check_common:
static int do_check_common(struct bpf_verifier_env *env, int subprog) |
首先准备一个state;然后根据函数类型和参数类型设置reg;
do_check
之后调用do_check:
static int do_check(struct bpf_verifier_env *env) |
do_check_common是针对每个subprog只调用一次的,但后在do_check_common中调用了do_check,即do_check也是对于每个subprog都只调用一次的;
在do_check内部,会从头开始遍历依次所有指令,首先进入is_state_visited函数,这个函数仅对prune_point有效,不是prune_point的会立即退出;然后这里的遍历指令不是简单的顺序遍历就完事了,这要充分考虑多种情况:条件跳转、直接跳转、exit;
在env中会维护一个stack,然后通过env->stack_size表示栈中元素的个数,env->head表示栈头,然后通过单链表的形式组织elem们进入栈;
当do_check遇到了条件跳转会进入到check_cond_jmp_op函数中,如果确定两个分支都会走到,则会先通过mark_chain_precision函数来修改precise标记,然后将true分支压入栈中,

上面这段代码,走到exit时会走下来,出栈一个指令继续分析;比如is_state_visited返回为true,那么就调到这里,直接分析下一个;同样,如果是条件跳转的false分支分析完了,进入到exit了,那么下面pop出来的就是true分支了;
is_state_visited
static int is_state_visited(struct bpf_verifier_env *env, int insn_idx) |

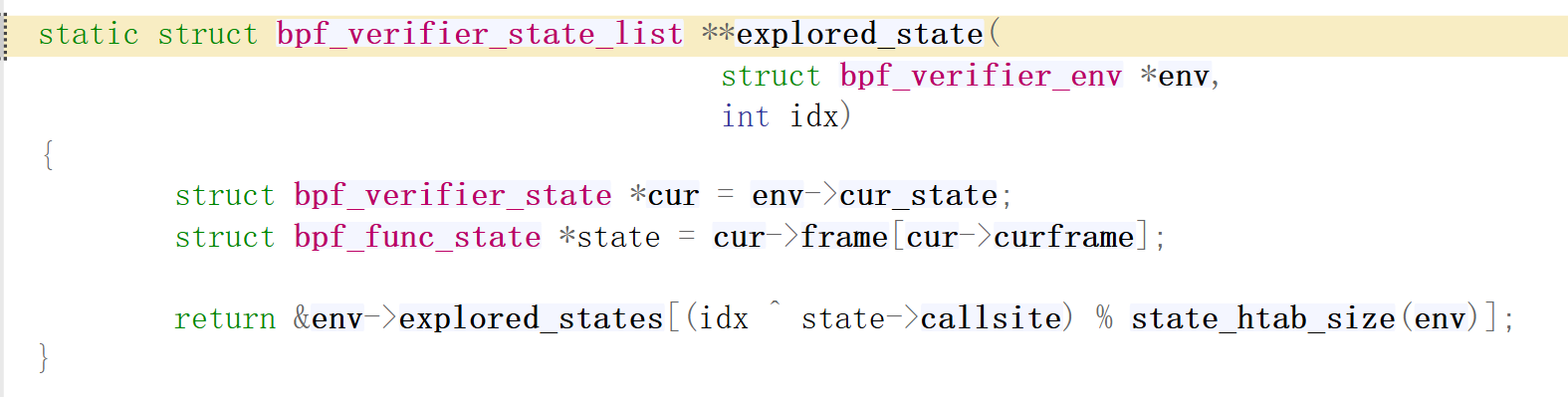
对于is_state_visited这个函数的理解,重点在于bpf_verifier_state_list这个结构,首先在env中存在一个名为explored_states的bpf_verifier_state_list类型数组,该数组的每一项要对应一个调用者和一个被调用者,因此搜索空间非常巨大,所以要采用哈希表的形式来存储;
在最开始的情况下,获取到一个空链表项,直接跳过前面的代码,看add_new,先分配一个新的链表项new_sl,然后将当前的state情况copy进去,链进链表中:

进入到is_state_visited函数中,首先就要获取这样一个链表,(当然它可能为空),然后开始遍历其中的每一个state,因为这些state其实都是相同的调用者和相同的被调用者了;
copy
看一下这个new_sl是如何创建与初始化的:
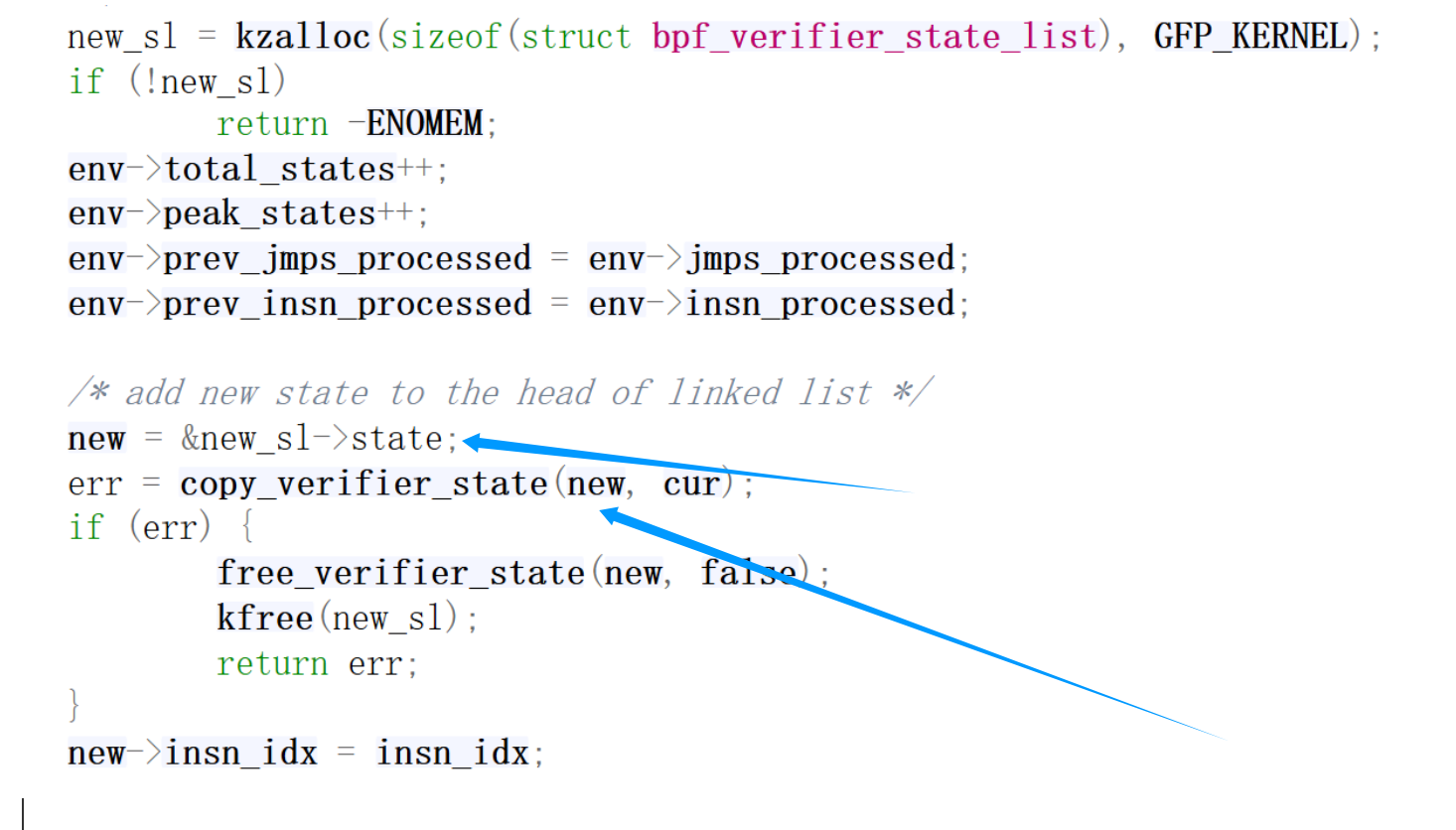
传递new进去copy:
static int copy_verifier_state(struct bpf_verifier_state *dst_state, |
之后回来继续:

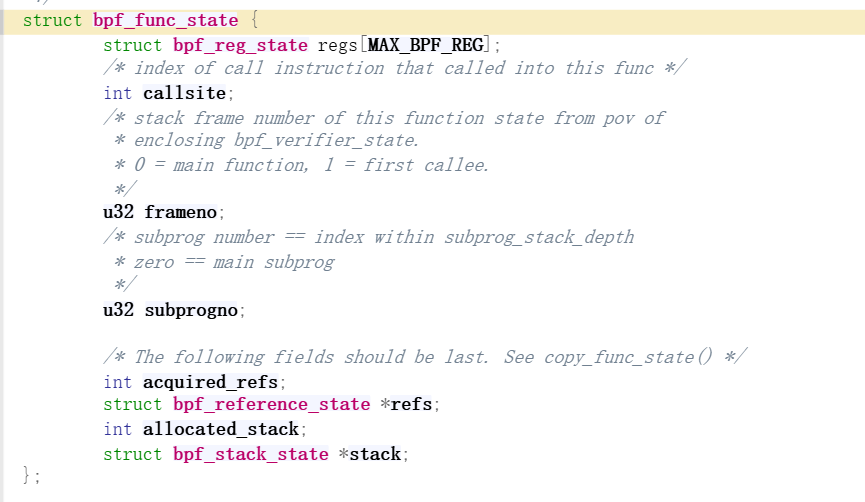
关于frame的定义如下:

states_equal
好下面看如何判断两个state相同:
static int is_state_visited(env, env->insn_idx){ |
总结

bpf_check(){ |
precise的理解
首先在regsafe的检查中是先看reg的所有估计值和var_off的,如果完全一样直接认为是safe的(除了stack还要再检查一个frameno);如果存在不一样的地方,则检查type,这个precise是只针对标量有检查意义的;(因此,可以将precise理解为一个分支优化时对scalar的检查标准,如果是precise=false说明不必较真)
执行do_check_common->do_check->is_state_visited发现没有visit过,就要将当前state加入到链表中,这个时候就有了这次跳转(刚jmp,还没有执行任何新的指令)时的状态(可以理解为拍了一个快照一样保存到了sl中);
至于在对具体的指令进行分析,例如在条件跳转时要给src_reg标注精确,这个时候到了跳转进新的基本块的时候,这个标注就会带来,然后就会对src_reg的值进行严格检查,不精确就不让优化掉;
对于frame的理解
首先看eBPF的官方文档:
https://www.kernel.org/doc/html/latest/bpf/verifier.html |
主要就是说了一个state,如果call一个函数了,那么就会创建一个新的frame,通常frame0都是给自己的,然后新的frame1给被调用者,此时复制frame0的r1r5给frame1作为参数传递,r0/r6r9对frame1来说是null,
看check_func_call函数:
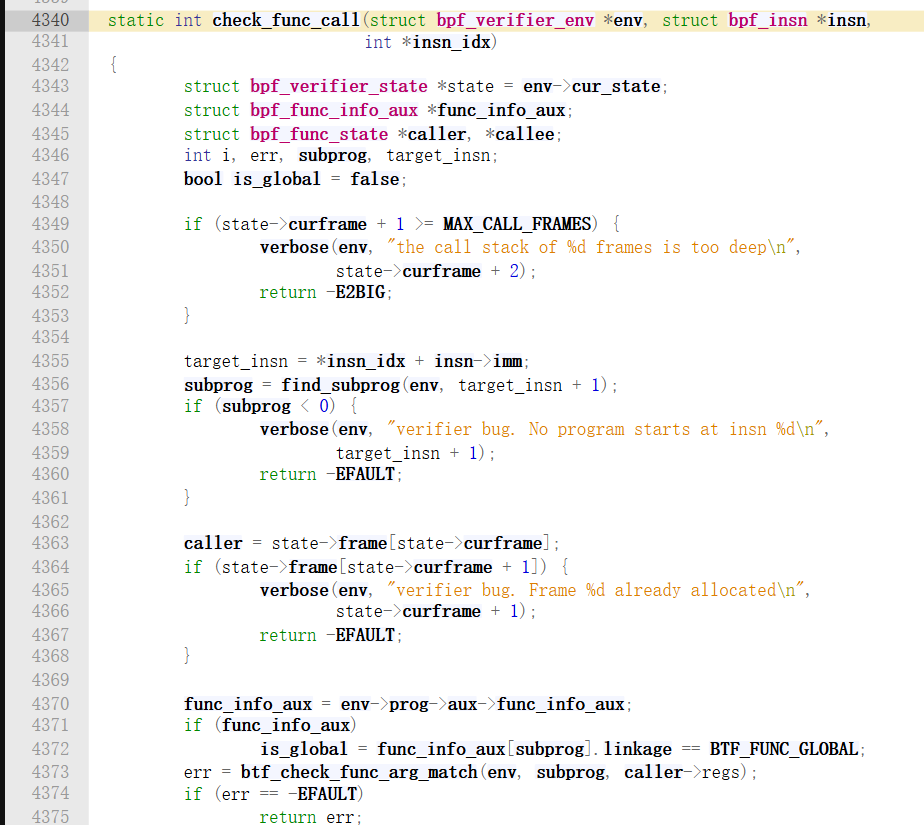

可以看到创建一个新的frame之后,将state的curframe切换到新的栈中,PC也到了被调用函数中了;
state只有subprog才会创建新的(在do_check_common函数中切换env->cur_state);
而subprog的标准是call | jmp32 以及src_reg == BPF_PSEUDO_CALL; 即eBPF到eBPF的函数调用,区别于辅助函数;所以只有内部的call才会被切分成subprog;
再看prune:而所有的跳转分支则也会标记为prune_point,所以prune_point是subprog的超集;
所以就明朗了,其实 is_state_visited 中的比较、失败后的new_sl的copy、以及__mark_chain_precision都是围绕着frame来的!
只有func_state中才会有regs,bpf_verifier_state中包s含func_state,但是没有regs;
mark_chain_precision调用情况总结
check_stack_write:写栈上写8字节;
static int __mark_chain_precision(struct bpf_verifier_env *env, int regno, |
在当前state中先回溯,到第一条指令后对reg们进行标记,reg_mask和stack_mask还不为0,就得继续向上回溯parent;



